From cloud-native innovation to enterprise standard: The rise of the S3 API as a core storage layer
When Amazon Web Services (AWS) launched Simple Storage Service (S3) in 2006, it signalled a groundbreaking shift in the way data is stored, accessed, and managed. Initially regarded as a niche offering designed for cloud-native workloads, the S3 API has since evolved into the industry-standard interface for object storage. Today, it stands as a robust, highly scalable, and cost-efficient storage layer, increasingly adopted not only in the public cloud, but also across hybrid IT infrastructures and even within on-premises enterprise environments.
The enduring appeal of the S3 API lies in its simplicity, scalability, and platform-agnostic design. By abstracting the complexity of underlying infrastructure and enabling HTTP-based access to objects within buckets, it allows for effortless integration across a wide variety of software platforms and enterprise use cases. These include backup and archival solutions, media repositories, data lakes, and analytics platforms.
Thanks to its stateless, RESTful architecture, the S3 API is ideally suited for distributed workloads, DevOps environments, and cloud-native applications. Additionally, a comprehensive ecosystem of tools, SDKs, and third-party integrations ensures that it remains highly accessible and developer-friendly.
Data Growth Demands Scalable Storage
The demand for scalable, flexible storage models has never been more critical. Global data volumes continue to double every few years, fuelled by the rapid increase in machine-generated data, AI training datasets, surveillance footage, and regulatory compliance requirements.
Yet despite this explosion in data creation, only an estimated 10 to 20 percent of stored information is actively used at any given time. Furthermore, the window in which data remains “hot” or frequently accessed has dramatically decreased—from months or years to just days or weeks in many cases.
This evolving pattern reinforces the importance of tiered storage architectures. Businesses must be able to differentiate between high-value, time-sensitive data and long-term, infrequently accessed information. While hot data demands high-speed, low-latency access, the majority of data can be efficiently stored using durable, cost-effective object storage solutions—such as S3-compatible platforms—designed specifically for cold or inactive data.
80 % of your data is inactive
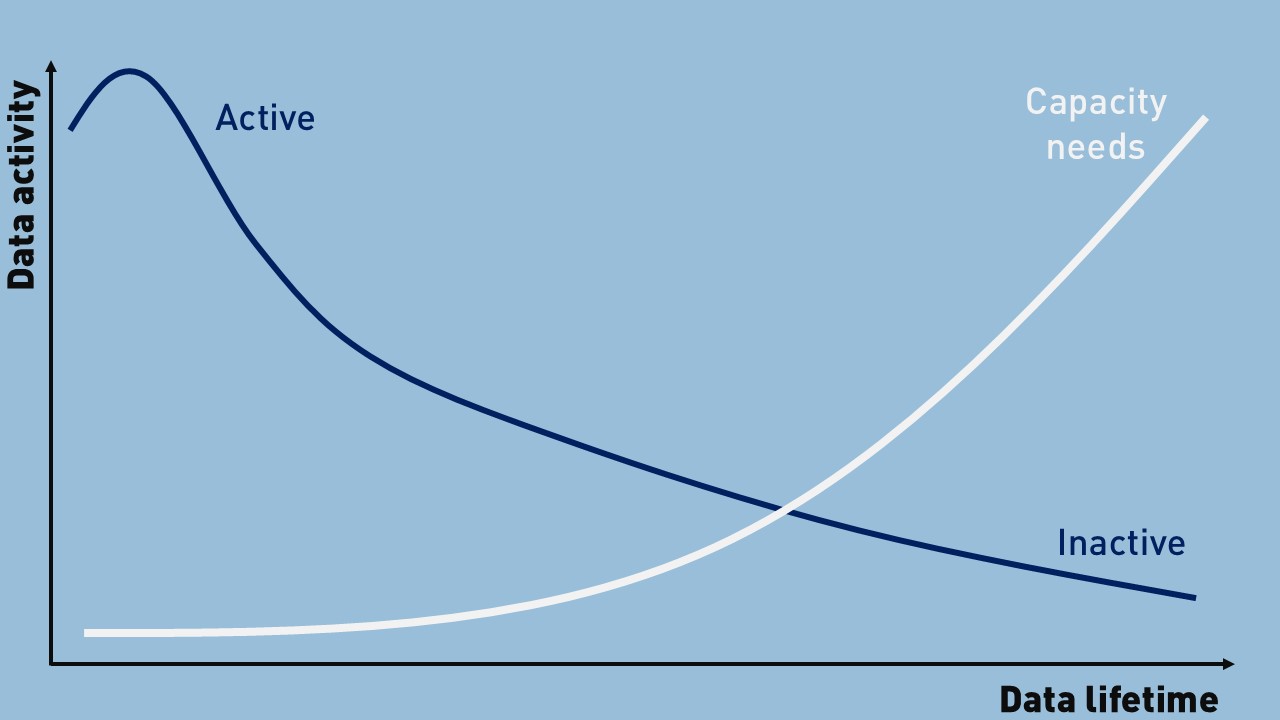
As the vast majority of enterprise data is now considered inactive or “cold”, yet must still be retained, protected, and readily retrievable, organisations are being forced to rethink traditional high-performance storage models. Relying on expensive, low-latency storage systems for large volumes of low-access data has become increasingly economically unsustainable, especially in the face of explosive data growth.
The rising adoption of S3-compatible object storage offers a compelling alternative—but it also raises a critical question for IT decision-makers:
How does S3-compatible storage compare to traditional block-level enterprise storage systems—those high-performance, low-latency platforms that have long served as the foundation of mission-critical IT infrastructures?
Why S3-compatible storage is taking over the data centre
-
Scalability
Virtually limitless storage capacity with horizontal scalability that allows organisations to expand on demand—without downtime or disruption. -
Cost Efficiency
Designed for capacity-based pricing, S3-compatible storage supports tiered storage models (hot, cold, archive) to optimise costs based on data access patterns. -
Simplicity and Flexibility
Enables self-service provisioning and API-driven access, making integration easy across diverse workloads and platforms. -
Resilience and Durability
Ensures high data availability and integrity through built-in redundancy, replication, or erasure coding—even at petabyte scale. -
Multi-Tenancy and Enterprise Security
Offers fine-grained access controls, server-side encryption, and audit logging, supporting secure, multi-tenant environments. -
Cloud-Native Integration
Seamlessly integrates with cloud platforms, modern application frameworks, and DevOps pipelines, supporting a wide range of hybrid and cloud-native architectures.
When S3 falls short: What you shouldn’t overlook
-
Latency and Performance Constraints
S3-compatible object storage is not designed for high IOPS or low-latency transactional workloads, making it unsuitable for databases or real-time processing tasks. -
Consistency Models
Many object storage platforms operate under eventual consistency, which can pose challenges for applications that require strict transactional integrity and immediate consistency. -
Protocol Overhead
Accessing data over HTTP/S protocols introduces latency and processing overhead, especially when compared to direct-attached or SAN-based block storage systems. -
Compatibility with Legacy Applications
Traditional enterprise applications—particularly those built around file or block storage paradigms—may require significant refactoring or middleware solutions to interface with S3 APIs effectively.
Block Storage Still Has Its Place
Block-level storage remains the preferred choice for databases, virtualization platforms, and latency-sensitive workloads. With guaranteed performance metrics (QoS), rich RAID functionality, and proven integration in existing IT landscapes, block storage continues to serve a critical role in many enterprise architectures. But the real question is for what purpose and at what cost?
That said, the architecture of S3-compatible storage introduces a more future-proof paradigm, especially for that 80-90 % of the data that is inactive but still mission-critical as data volumes and processing demands grow. Unlike traditional block storage—which relies on a centralised controller and tightly coupled infrastructure—S3 leverages parallel storage processing and stateless interactions. This allows clients to read and write data concurrently across distributed nodes, eliminating the typical I/O bottlenecks of monolithic systems. Moreover, intelligence is shifting toward the client side: modern applications and backup solutions are increasingly capable of handling tasks like chunking, deduplication, and retry logic independently. This architectural separation of data and control planes enables unmatched scalability and flexibility, making S3-based storage inherently more adaptable for cloud-native, AI-driven, and data-intensive workloads of the future.
Continuous Protection at the Object Level
Another critical advantage of S3-compatible storage lies in how it handles data protection. Traditional SAN systems rely heavily on scheduled snapshots at the volume level, which capture the entire dataset at a given point in time. While effective, this model introduces gaps between snapshots and lacks granularity—restoring a single file often means recovering an entire volume or navigating complex backup sets. In contrast, S3 storage brings built-in, per-object versioning and retention policies. Each object can have multiple historical versions preserved automatically, offering true continuous data protection. Combined with object lock features, this enables compliance-grade immutability and recovery at the file level, reducing data loss risk and improving recovery time objectives dramatically. It is a model far better suited to today’s real-time, high-volume, and compliance-sensitive environments.
In conclusion
As data volumes grow and application architectures evolve, the limitations of legacy storage models become more apparent. S3-compatible object storage has proven itself to be more than a cloud-native convenience—it is a scalable, flexible, and cost-efficient foundation for modern data management. From granular, object-level protection to client-side intelligence and parallel access models, S3 aligns closely with the demands of real-time analytics, compliance, and hybrid cloud strategies. While traditional block storage still plays a crucial role in latency-sensitive workloads, the future of large-scale, sustainable data storage is increasingly defined by the strengths of the S3 API.

Vincent van der Linden
Regional Sales Manager, RNT Rausch GmbH
Know-how about digitalisation, servers and storage

NIS2 made easy: Immutable storage contributes to compliance
The new NIS2 Directive presents companies with the challenge of enhancing their cybersecurity measures and ensuring data integrity. With immutable storage, businesses can ensure that critical data is permanently protected and cannot be altered. This technology not only provides increased security but also meets the stringent requirements of NIS2.
Discover how immutable storage can help your company comply with the directive while safeguarding your sensitive information.
NIS2 Directive: Cybersecurity requirements and impact on businesses
There are many reasons why companies have cause for concern these days —…
5 reasons to choose AMD EPYC™ 9005 processors
In the world of data centers, there is a constant race for higher performance,…
Mountain School in the Dominican Republic
A school with a different concept. Instead of the traditional curriculum that…
Foundation for the security of IT ecosystems
In a data-driven world, opportunities and risks are rising equally. AMD…
ISC High Performance
May 12th- May 16th, 2024 Come and see us in Hamburg at the event for…
Pyramid Computer GmbH integrates RNT
Pyramid Computer integrates RNT Rausch, expanding its portfolio with leading…







